HRV Setup in Ponemah 6.x
To use Variability Analysis, at least one channel needs to be set to ECG, BP or LVP for the analysis option.
Configuration
- Start a Review Session by selecting Actions | Start Review
- Select the desired Subjects, Channels, and Time Range
(see the Loading Data into Review section of the manual for details.) - Select Setup | Variability Analysis…
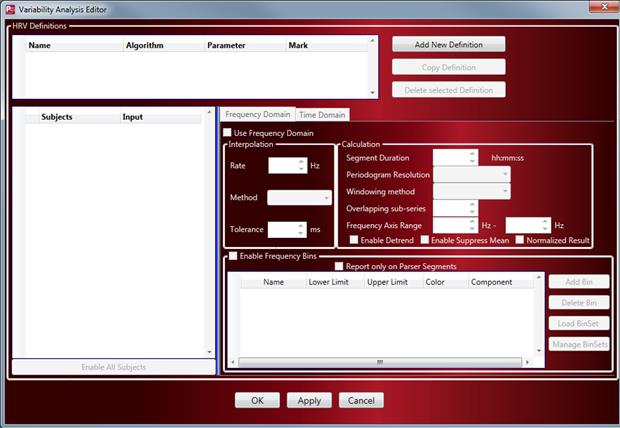
-
Select the Add New Definition button.
A new HRV Definition will be added for configuration. HRV Definitions, allow you the user to configure multiple analyses based on different setting selections for additional analysis results reporting or to compare results.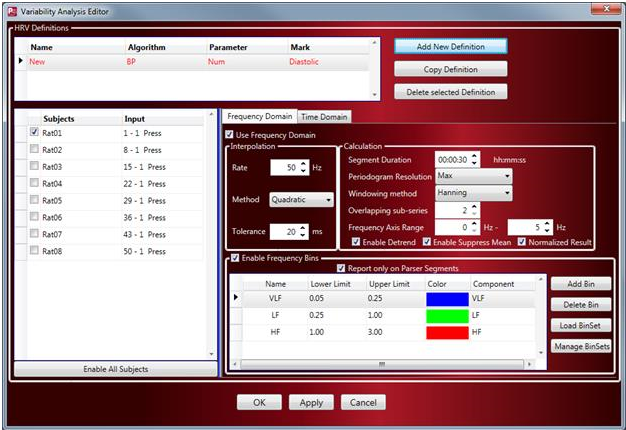
-
From the HRV Definitions settings box, enter a unique Definition Name, select the Algorithm, Parameter, and Mark to use.
Algorithm
Defines the analysis module this definition will use for the HRV analysis. If deriving HRV from ECG, choose ECG as the Algorithm. If deriving HRV from blood pressure, choose BP as the Algorithm.
Parameter
Defines the parameter used for the variability analysis. RR-I is typically used for ECG, while IBIms is typically used for Blood Pressure.
Mark
Used as the time stamp for reporting parameter data. Typically, the R-wave is used for ECG, while Diastolic is typical used for Blood Pressure.
- Select the Subjects to analyze with the defined HRV settings using the checkboxes associated with the Subject IDs listed.
- Select the dropdown menu under the Input column to choose the channel to analyze. The Input dropdown menu will only list channels associated with the Algorithm selected; e.g. if BP is selected as the Algorithm, only BP channels will be listed. This is important if the implant being used has multiple ECG or BP channels to ensure the intended channel is the one being analyzed.
- If interested in HRV Analysis using the Frequency Domain, enable the checkbox associated with Use Frequency Domain.
a. Define the Interpolation settings. This will equally space the selected data series to accurately calculate the Periodogram.
Rate
Defines the numerical frequency value used for the interpolation interval.
Method
Defines the interpolation method. Options include Linear, Quadratic and Cubic.
Tolerance
Allows the user to permit interpolation over data gaps to prevent aborting analysis of the segment when Bad Data Marks are encountered. Default is 20 milliseconds. Time entry format: ss.mmm.
b. Define the Calculation settings used to calculate a high resolution Periodogram of the selected data. The Periodogram splits the data into multiple overlapping windows (smaller data sets or sub-series) and performs a mathematical operation called a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) on each sub-series.
Segment Duration
Time interval used for Variability Analysis calculations. The segment duration is different from the Logging Rate used in other areas of Ponemah.
Periodogram Resolution
Defines the number of points used to calculate the Periodogram.
Windowing Method
The mathematics behind the FFT assumes that the input waveform repeats cyclically. This is not the case with most waveforms, so to avoid sharp discontinuities that would cause additional frequency components in the result, a windowing method is used. Windowing is used to taper the sub-series endpoints to better approximate a truly periodic signal. By tapering the window smoothly to zero at each end, the height of the side lobes resulting from a rectangular window can be diminished; this is achieved at the expense of a wider main lobe (coarser response at the true center frequency). Choose a windowing method to define how the time domain signal will be truncated. Options include:
Rectangle - This windowing method does not modify the data signal and produces the sharpest spectral peaks, but produces the worst side lobes due to ‘border artifact’.
Hanning - Similar to a bell curve, this windowing method provides greater weighting for points in the center of the window. This is a good general-purpose window; however, it does remove most of the signal. If unsure about which window would be best, try this one first. In comparison with the rectangular window, it reduces border artifact by virtue of its smaller first side lobe amplitude. However, non-rectangular windowing affects the average power of a signal because some of the time samples are attenuated when multiplied by the window.
Hamming - Similar to the Hanning window, this windowing method provides another way to taper endpoints of the sub-series and preserves more of the original signal than a Hanning window, but at the price of unpleasant side lobes. The Hamming window has slightly more attenuation in the first side lobe than the Hanning window, but the subsequent side lobes trail off more slowly than with the Hanning window.
Overlapping Subseries
Used to subdivide the data segment into smaller segments that are windowed individually to provide the desired frequency resolution. Values can be between 2 and 50.
Frequency Axis Range
Range of the x-axis to display the Periodogram data.
Detrend
Removal of any baseline wander in the data.
Suppress Mean
Removes the baseline offset so that all data averages to 0. Enabling this option helps to ensure precise statistical measures.
Normalized Result
Normalizes the Periodogram result so that the maximum y-axis value is equal to 1.
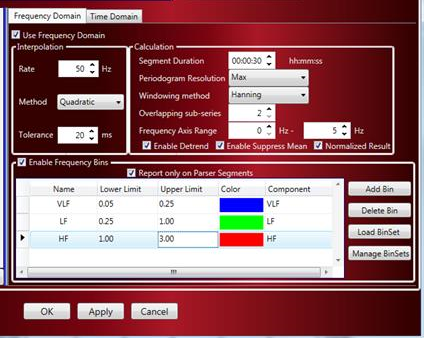
c. Enable Frequency Bins to create a Periodogram. The power contained within each of the bins is determined and used for further analysis. The default values provided in the list are examples and may be adjusted.
Enable Report only on Parser Segments to only report HRV Frequency analysis results from waveform data contained within defined Parser Segments. This is important as it allows the use to have equally spaced segments of data that should be signal noise free to ensure the Periodogram are accurate. Noise within the waveform segment select will lead to unexpected results.
To setup the Frequency Bins, define the following items:Name
Name assigned to the frequency bin. Default values are shown, but can be changed by clicking within the box that contains the name.
Lower Limit
Numerical frequency value used for the Lower Limit for the specific frequency bin. The Lower Limit must be less than the Upper Limit. The value can be changed by clicking within the box that contains the Lower Limit value.
Upper Limit
Numerical frequency value used for the Upper Limit for the specific frequency bin. The Upper Limit must be greater than the Lower Limit. The value can be changed by clicking within the box that contains the Upper Limit value.
Color
Color used on graph pages for the specific frequency bin. The color can be changed by clicking on the color box.
Component
The Variability Analysis calculates parameters specific for HRV. For the calculations to perform correctly, the specific frequency components must be identified. Options are ULF, VLF, LF, HF and Unspecified. The Unspecified option is the only frequency option that can be used more than once. For the named frequency components, the Upper Limit of VLF must be less than the Lower Limit for LF and the Upper Limit for LF must be less than the Lower Limit of HF.
Add Bin
Used to add additional frequency bins.
Delete Bin
Used to delete additional frequency bins.
Load BinSet
Selecting the Load BinSets button will display the available, predefined frequency bin sets. Mouse and Rat bin sets are available as defaults. However, any user-defined bin set will be listed if they exist. Selecting the bin set will load it into the Variability Analysis Editor dialog for use with the currently displayed HRV Definition analysis.
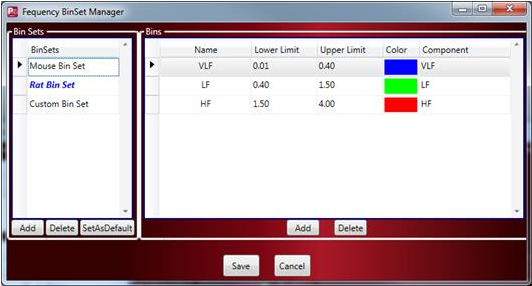
Manage BinSets
Choosing Manage Bin Sets … will display the Manage Frequency Bins dialog. This displays the bin sets available for use and allows the user to create customer bin sets for easy selection. The default bin set used for calculations can be customized by selecting the desired bin set to load by default and then selecting the SetAsDefault button. The default bin set is identified by bold, blue font.
-
If interested in HRV Analysis using the Time Domain, select the Time Domain tab and enable the checkbox associated with Use Time Domain.
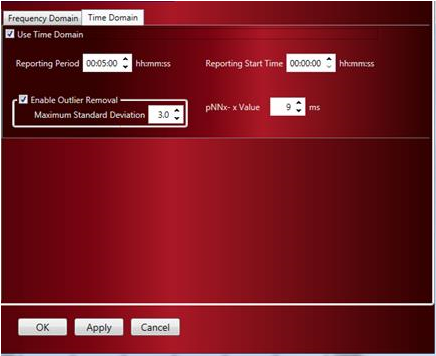
Configure the following Time Domain settings:
Reporting Period
Defines the rate at which data is reported to the Variability Analysis Derived List Views.
Report Start Time
This defines the time offset at which to start reporting Time Domain HRV Results to the Derived List View. For example, if the experiment data is loaded at 7:00 AM but you want the analysis to start at 10:00 AM, then enter a Report Start Time of 03:00:00 to indicate a 3 hour offset.
pNNx – x Value
The time, in milliseconds, used to calculate the number of valid adjacent NN values not separated by data breaks or bad data marks that differ by more than this value. The number of counts based on this setting are reported as the Derived Parameter NNx.
Note: Default values by species are:
a. Mouse 6 milliseconds
b. Rat 9 milliseconds
c. Monkey 25 milliseconds
d. Dog 50 milliseconds
Outlier Removal
Enable the checkbox for Enable Outlier Removal and define the Maximum Standard Deviation above which values will be removed.
Note: Outlier Removal is disabled by default.
Comments
0 comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.