Minimizing Postoperative Complications in Mice
Intraperitoneal (IP) Device Placement
Intraperitoneal rather than subcutaneous device placement can reduce post-operative complications in mice. Note: for IP placement, mice must be 25 grams or greater in size. The complications that may arise with this device placement are typically easier to manage and are not as detrimental to the animal.
Complications and Treatment:
Monitor for and address these issues daily.
- Mild to Moderate Paraphimosis (male mice)
- Moisten with warm sterile saline
- Replace penis within prepuce
- Liberally apply Artificial Tear Ointment (Covetrus) to the prepuce
- Proteinaceous Penis Plugs (male mice)
- Most likely to occur in first 3 days of post-operative period, but may occur up to 7 days post-op
- Palpate the prepuce to check for presence of proteinaceous penis plugs as they are sometimes contained within the prepuce
- Moisten the prepuce with warm sterile saline to loosen the plug
- Gently pull on the plug to remove it from the penis
- Note if the animal’s body or extremities feel cool to the touch
- Proteinaceous plugs can cause a decrease in activity due to discomfort
- If cool, place animal’s home cage half on a heating pad set to low to aid in animal’s self-regulation of
- Check hydration by tenting the skin
- If dehydrated, administer 3cc warm sterile saline SQ for hydration
- Proteinaceous plugs can cause a decrease in activity due to discomfort
Subcutaneous (SQ) Device Placement
Subcutaneous device placement can allow for the implantation of mice smaller than 25g but can result in more serious post-operative complications.
Reducing Complications Resulting from Subcutaneous Device Placement:
- During surgical preparation:
- Clip the fur over the right flank where the device will be after implantation
- Take care not to nick the skin when clipping
- This allows for the skin condition to be more easily monitored post- operatively
- Prophylactically apply 1% Silver Sulfadiazine Cream (SSD) to the clipped area of skin on the animal’s flank
- This allows time for the cream to soak into the skin during surgery prior to the animal waking up from anesthesia
- Clip the fur over the right flank where the device will be after implantation
- During Surgery:
- When making the subcutaneous pocket for device placement:
- Always place the device on the animal’s right side
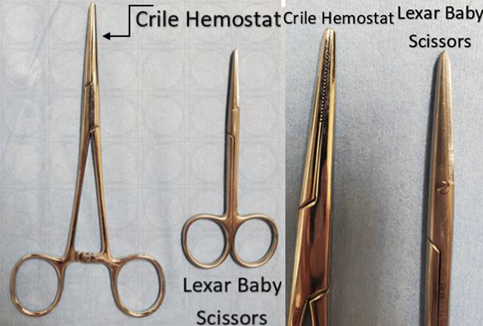
- Use a Crile hemostat rather than Lexar baby scissors to make the pocket
- Have the handle rings parallel to the table when starting the pocket so that there is enough space cleared for the device to make it past the forelimb
- Stay superficial so as not to puncture the jugular during this process
- Once the pocket has been made to pass the forelimb, change the orientation of the Crile hemostats so that the handle rings are perpendicular to the table
- This will help keep the pocket on the flank of the animal and not on the ventral surface
- Make the pocket very large to reduce pressure placed on the skin from the device – a good representation of size approximation is to create a pocket and ensure that a 3cc syringe can slide in comfortably.
- When making the subcutaneous pocket for device placement:
Complications and Treatment:
Monitor for and address these issues daily.
- Dryness, thinning, redness, and/or irritation to the skin over the device pocket
- Liberally apply 1% Silver Sulfadiazine Cream (SSD) to the irritated skin
- Continue to observe carefully for changes and re-apply SSD daily until issue is resolved
- Adherence of device to skin over the device pocket – will likely accompany one or multiple of the previously mentioned symptoms
- Anesthetize the animal if necessary
- Place gauze soaked in warm sterile saline over adhered area to moisten and loosen skin
- Full moistening may take several minutes; the skin should appear hydrated and fuller
- Gently massage the area until skin is free from device
- Carefully inspect for any openings in the skin
- Liberally apply 1% Silver Sulfadiazine Cream (SSD) to the irritated skin
- If the skin opens while freeing the device while the animal is anesthetized, you can repair the opening
- Clean area with a combination of saline and chlorhexidine scrub
- Thoroughly lavage the opening in the skin
- Remove any thin or necrosed tissue
- Place 2 to 3 sutures in a horizontal mattress pattern or another tension-relieving suture pattern to close the skin
- Male mice typically tolerate this well
- In our experience, female mice tend to be more likely to remove sutures which necessitates euthanasia
- Consider placing intradermal sutures in female mice
- Apply a thin line of a flexible tissue adhesive, such as Gluture, along the wound closure
If skin was found open in the animal’s cage, euthanasia is recommended due to high risk of infection.
Can't find what you're looking for? Contact Us
Comments
0 comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.